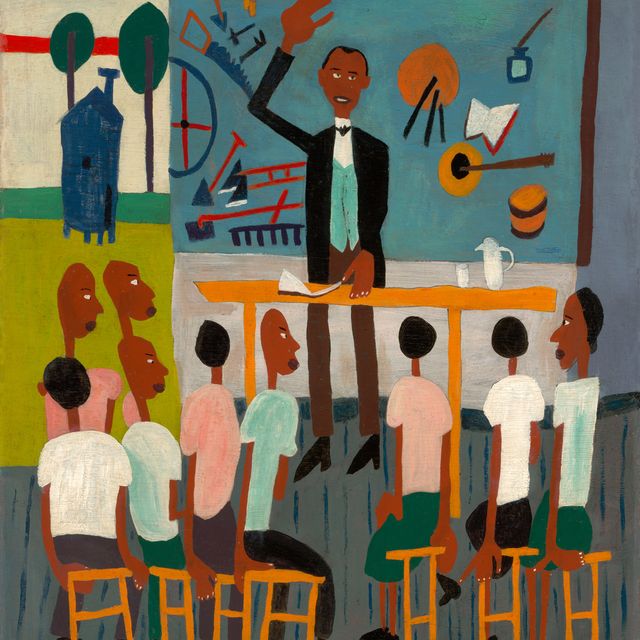Jacob Lawrence

- Born
- Atlantic City, New Jersey, United States
- Died
- Seattle, Washington, United States
- Active in
- New York, New York, United States
- Seattle, Washington, United States
- Biography
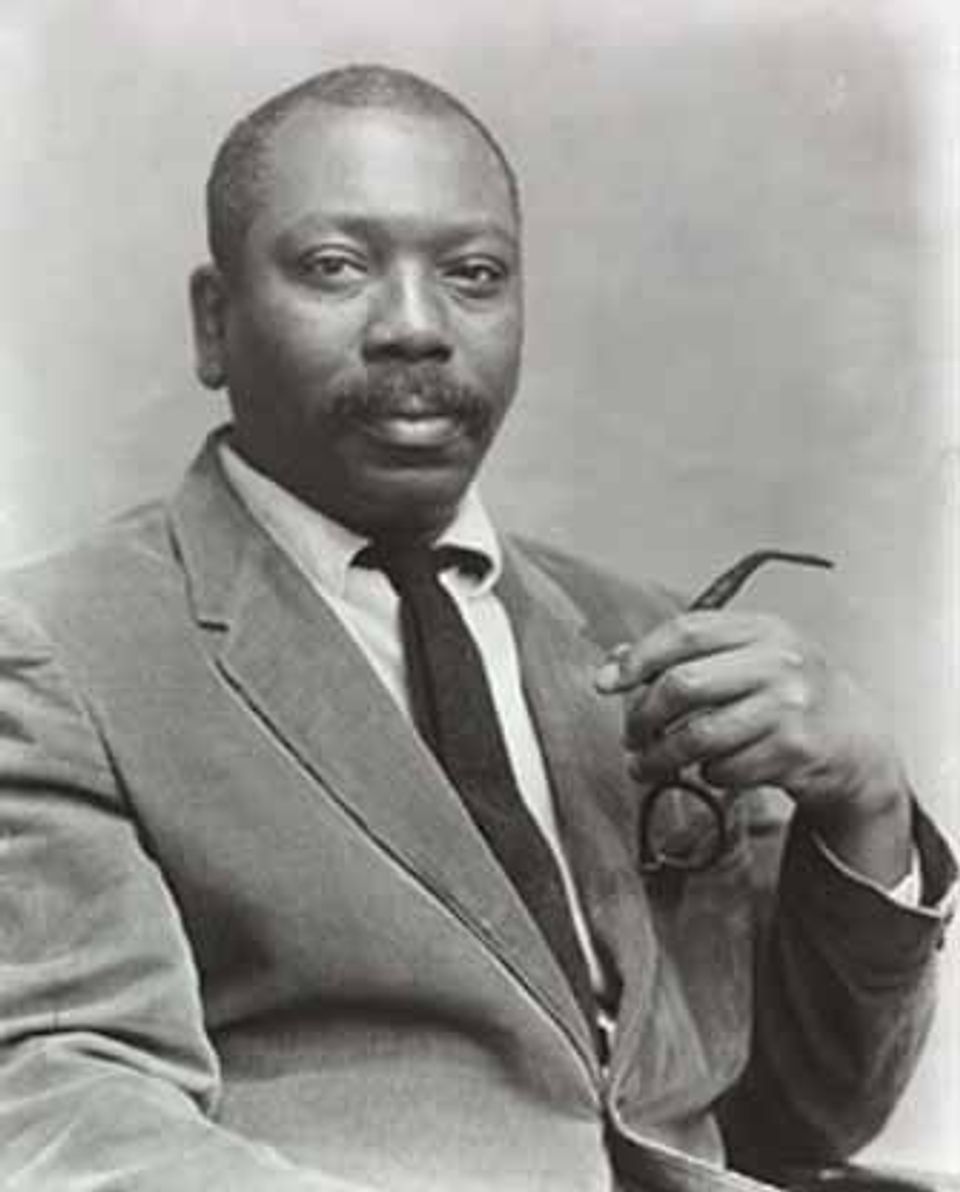
Painter. A social realist, Lawrence documented the African American experience in several series devoted to Toussaint L'Ouverture, Frederick Douglass, Harriet Tubman, life in Harlem, and the civil rights movement of the 1960s. He was one of the first nationally recognized African American artists.
Joan Stahl American Artists in Photographic Portraits from the Peter A. Juley & Son Collection (Washington, D.C. and Mineola, New York: National Museum of American Art and Dover Publications, Inc., 1995)
- Artist Biography
"If at times my productions do not express the conventionally beautiful, there is always an effort to express the universal beauty of man's continuous struggle to lift his social position and to add dimension to his spiritual being." -- Jacob Lawrence quoted in Ellen Harkins Wheat, Jacob Lawrence: The Frederick Douglass and Harriet Tubman Series of 1938-40 (Hampton, Va.: Hampton University Museum; Seattle: in association with University of Washington Press, 1991), n.p.
The most widely acclaimed African American artist of this century, and one of only several whose works are included in standard survey books on American art, Jacob Lawrence has enjoyed a successful career for more than fifty years. Lawrence's paintings portray the lives and struggles of African Americans, and have found wide audiences due to their abstract, colorful style and universality of subject matter. By the time he was thirty years old, Lawrence had been labeled as the "foremost Negro artist," and since that time his career has been a series of extraordinary accomplishments. Moreover, Lawrence is one of the few painters of his generation who grew up in a black community, was taught primarily by black artists, and was influenced by black people.
Lawrence was born on September 7, 1917,* in Atlantic City, New Jersey. He was the eldest child of Jacob and Rosa Lee Lawrence. The senior Lawrence worked as a railroad cook and in 1919 moved his family to Easton, Pennsylvania, where he sought work as a coal miner. Lawrence's parents separated when he was seven, and in 1924 his mother moved her children first to Philadelphia and then to Harlem when Jacob was twelve years old. He enrolled in Public School 89 located at 135th Street and Lenox Avenue, and at the Utopia Children's Center, a settlement house that provided an after school program in arts and crafts for Harlem children. The center was operated at that time by painter Charles Alston who immediately recognized young Lawrence'stalents.
Shortly after he began attending classes at Utopia Children's Center, Lawrence developed an interest in drawing simple geometric patterns and making diorama type paintings from corrugated cardboard boxes. Following his graduation from P.S. 89, Lawrence enrolled in Commerce High School on West 65th Street and painted intermittently on his own. As the Depression became more acute, Lawrence's mother lost her job and the family had to go on welfare. Lawrence dropped out of high school before his junior year to find odd jobs to help support his family. He enrolled in the Civilian Conservation Corps, a New Deal jobs program, and was sent to upstate New York. There he planted trees, drained swamps, and built dams. When Lawrence returned to Harlem he became associated with the Harlem Community Art Center directed by sculptor Augusta Savage, and began painting his earliest Harlem scenes.
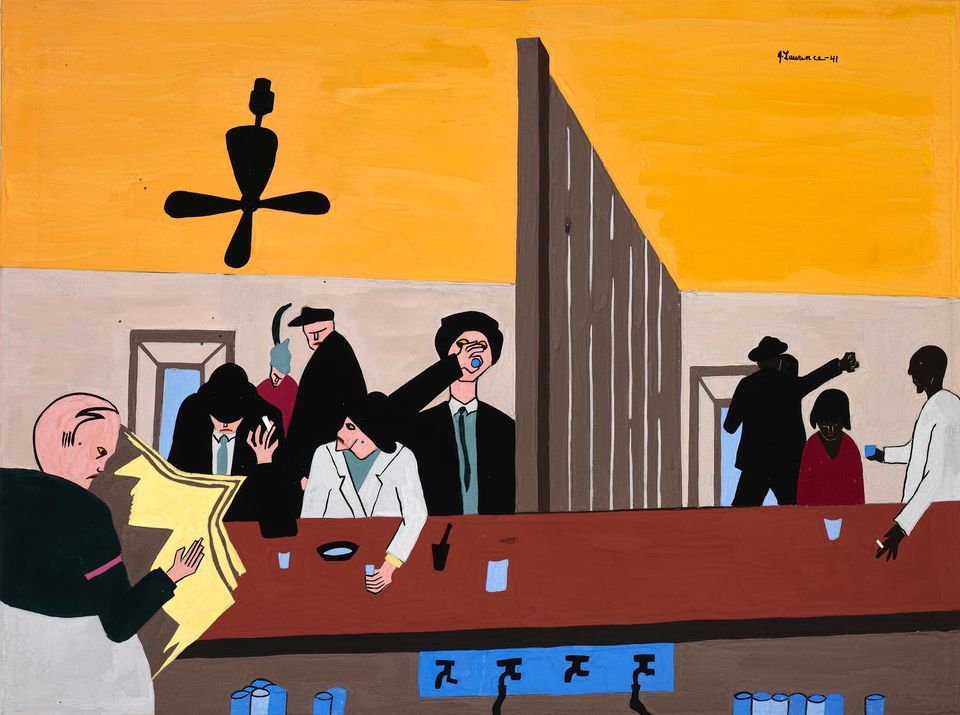
Lawrence enjoyed playing pool at the Harlem Y.M.C.A., where he met "Professor" Seifert, a black, self styled lecturer and historian who had collected a large library of African and African American literature. Seifert encouraged Lawrence to visit the Schomburg Library in Harlem to read everything he could about African and African American culture. He also invited Lawrence to use his personal library, and to visit the Museum of Modern Art's exhibition of African art in 1935.As the Depression continued, circumstances remained financially difficult for Lawrence and his family. Through the persistence of Augusta Savage, Lawrence was assigned to an easel project with the W.P.A., and still under the influence of Seifert, Lawrence became interested in the life of Toussaint L'Ouverture, the black revolutionary and founder of the Republic of Haiti. Lawrence felt that a single painting would not depict L'Ouverture's numerous achievements, and decided to produce a series of paintings on the general's life. Lawrence is known primarily for his series of panels on the lives of important African Americans in history and scenes of African American life. His series of paintings include: The Life of Toussaint L'Ouverture, 1937, (forty one panels), The Life of Frederick Douglass, 1938, (forty panels), The Life of Harriet Tubman, 1939, (thirty one panels), The Migration of the Negro,1940–41, (sixty panels), The Life of John Brown, 1941, (twenty two panels), Harlem, 1942, (thirty panels), War, 1946 47, (fourteen panels), The South, 1947, (ten panels), Hospital, 1949-50, (eleven panels), Struggle ?History of the American People, 1953–55, (thirty panels completed, sixty projected).
Lawrence's best known series is The Migration of the Negro, executed in 1940 and 1941. The panels portray the migration of over a million African Americans from the South to industrial cities in the North between 1910 and 1940. These panels, as well as others by Lawrence, are linked together by descriptive phrases, color, and design. In November 1941 Lawrence's Migration series was exhibited at the prestigious Downtown Gallery in New York. This show received wide acclaim, and at the age of twenty four Lawrence became the first African American artist to be represented by a downtown "mainstream" gallery. During the same month Fortune magazine published a lengthy article about Lawrence, and illustrated twenty six of the series' sixty panels. In 1943 the Downtown Gallery exhibited Lawrence's Harlem series, which was lauded by some critics as being even more successful than the Migration panels.
In 1937 Lawrence obtained a scholarship to the American Artists School in New York. At about the same time, he was also the recipient of a Rosenwald Grant for three consecutive years. In 1943 Lawrence joined the U.S. Coast Guard and was assigned to troop ships that sailed to Italy and India. After his discharge in 1945, Lawrence returned to painting the history of African American people. In the summer of 1947 Lawrence taught at the innovative Black Mountain College in North Carolina at the invitation of painter Josef Albers.
During the late 1940s Lawrence was the most celebrated African American painter in America. Young, gifted, and personable, Lawrence presented the image of the black artist who had truly "arrived". Lawrence was, however, somewhat overwhelmed by his own success, and deeply concerned that some of his equally talented black artist friends had not achieved a similar success. As a consequence, Lawrence became deeply depressed, and in July 1949 voluntarily entered Hillside Hospital in Queens, New York, to receive treatment. He completed the Hospital series while at Hillside.
Following his discharge from the hospital in 1950, Lawrence resumed painting with renewed enthusiasm. In 1960 he was honored with a retrospective exhibition and monograph prepared by The American Federation of Arts. He also traveled to Africa twice during the 1960s and lived primarily in Nigeria. Lawrence taught for a number of years at the Art Students League in New York, and over the years has also served on the faculties of Brandeis University, the New School for Social Research, California State College at Hayward, the Pratt Institute, and the University of Washington, Seattle, where he is currently Professor Emeritus of Art. In 1974 the Whitney Museum of American Art in New York held a major retrospective of Lawrence's work that toured nationally, and in December 1983 Lawrence was elected to the American Academy of Arts and Letters. The most recent retrospective of Lawrence's paintings was organized by the Seattle Art Museum in 1986, and was accompanied by a major catalogue. Lawrence met his wife Gwendolyn Knight, a fellow artist, when he was a teenager. They were married in 1941, and their close and mutually supportive relationship has been an important factor in Lawrence's career.
* "Free within Ourselves" catalog lists birth date as September 17, 1917, subsequent research determined the date should be September 7, 1917.
Regenia A. Perry Free within Ourselves: African American Artists in the Collection of the National Museum of American Art (Washington, D.C.: National Museum of American Art in Association with Pomegranate Art Books, 1992)
Luce Artist BiographyJacob Lawrence grew up in Harlem in the 1930s, where, despite the Depression, he found a “real vitality” among the black artists, poets, and writers in the community. He studied at the Harlem Art Workshop and joined the “306” studio, where he met his future wife, Gwendolyn Knight. Lawrence never completed high school but taught himself African American history, spending hours in the library researching legendary black figures and events to use in his paintings. He worked for the Works Progress Administration in the late 1930s and in 1941 was the first African American artist to be represented by a New York gallery. Lawrence created several series of paintings that documented the stories of heroes such as Harriet Tubman and John Brown. He considered his work to be celebratory and said once that his images “just deal with the social scene . . . They’re how I feel about things.” (Wheat, Jacob Lawrence, American Painter, 1986)