Sargent Johnson
- Also known as
- Sargent Claude Johnson
- Born
- Boston, Massachusetts, United States
- Died
- San Francisco, California, United States
- Biography
"It is the pure American Negro I am concerned with, aiming to show the natural beauty and dignity in that characteristic lip and that characteristic hair, bearing and manner; and I wish to show that beauty not so much to the white man as to the Negro himself." — Sargent Johnson quoted in San Francisco Chronicle,
- Luce Artist Biography
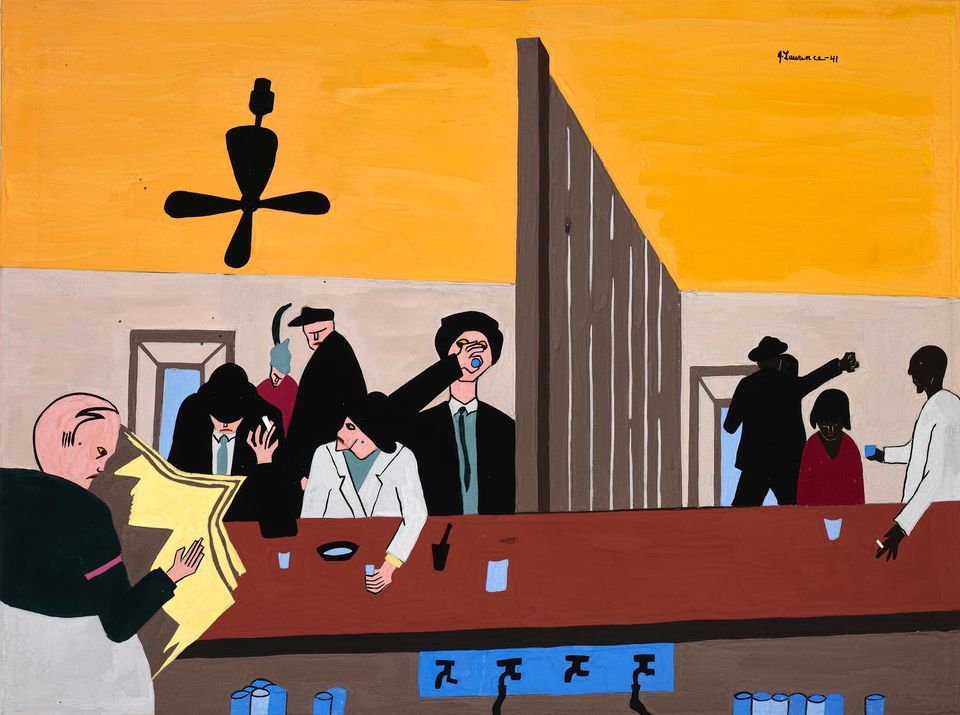
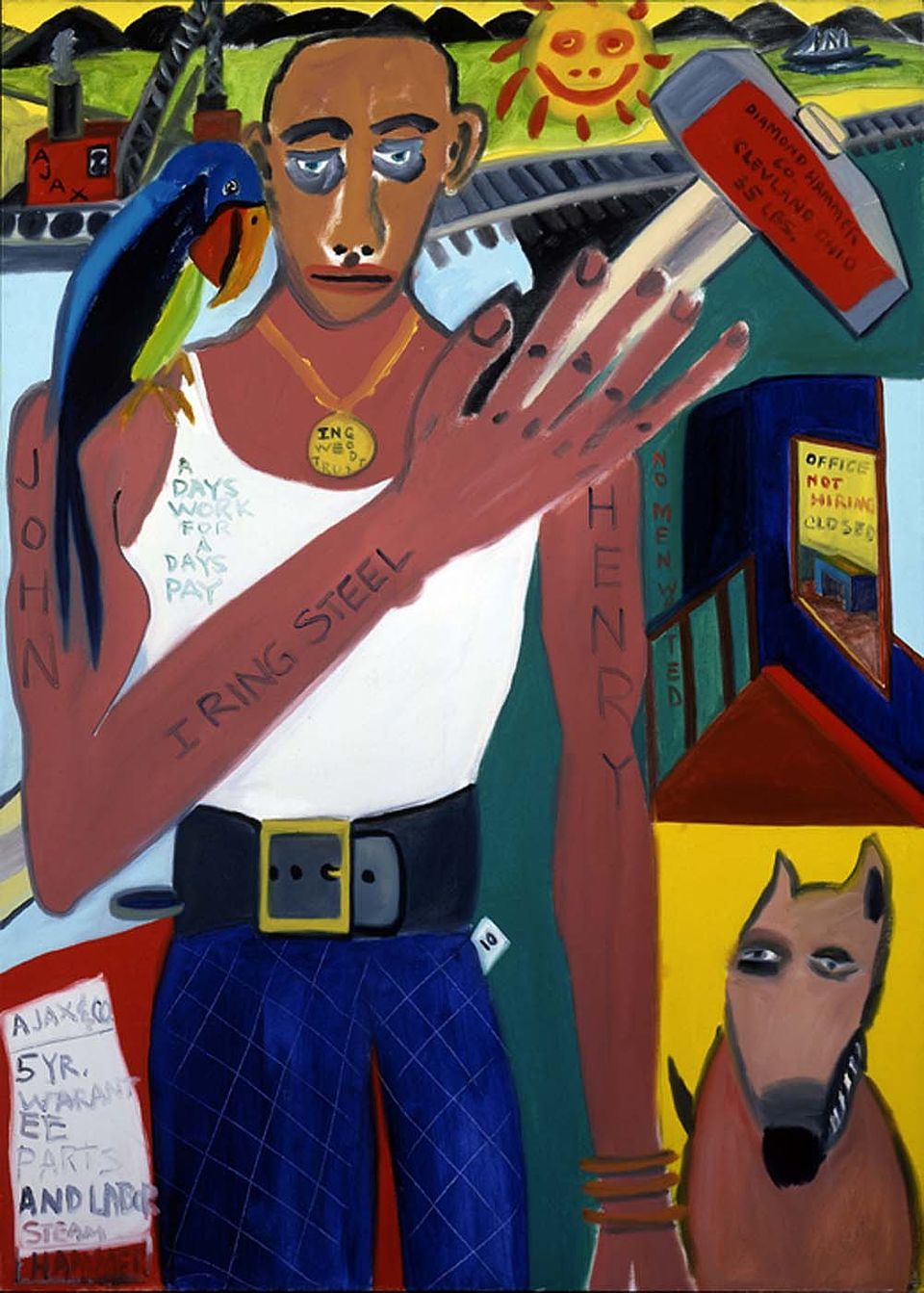
Sargent Johnson's first contact with art was through his aunt, the sculptor May Howard Jackson, who looked after him when he was young. Johnson's father was of Swedish ancestry and his mother was part Cherokee and part African American. While his brothers and sisters chose to be recognized as Native Americans or Caucasians, Sargent decided to live his life as a black man. He was orphaned in 1902 and lived in many different places before settling in North Beach, California. He created work for the Harmon Foundation, which supported African American art, and was also active in the Federal Art Project of the New Deal in the 1930s. Johnson's expressive sculptures in wood, terra-cotta, and clay explored his belief that "The Negroes are a colorful race; they call for an art as colorful as . . . can be made."