Gene Davis
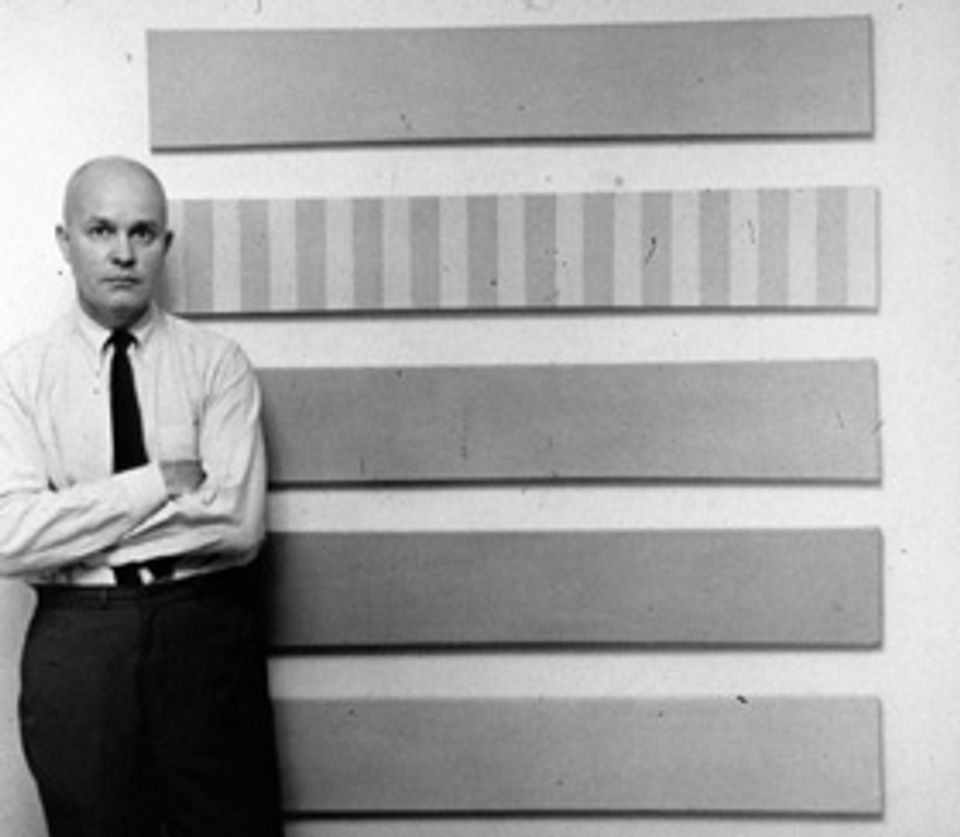

- Also known as
- Gene Bernard Davis
- Born
- Washington, District of Columbia, United States
- Died
- Washington, District of Columbia, United States
- Biography
[Gene Davis was] a major figure in 20th-century American painting whose contribution was invaluable in establishing Washington, D.C., as a center of contemporary art. Davis also played a significant national and international role in the color abstraction movement that first achieved prominence in the 1960s.
Born in Washington, D.C., Davis attended local schools and later worked as a sportswriter and White House correspondent before pursuing a career in art. Although never formally trained, Davis educated himself through assiduous visits to New York's museums and galleries as well as to Washington's art institutions, especially the Phillips Collection. He also benefited from the guidance of his friend Jacob Kainen, an artist and art curator.
Davis considered his nonacademic background a blessing that freed him from the limitations of a traditional art school orientation. His early paintings and drawings—though they show the influence of such artists as the Swiss painter Paul Klee and the American abstractionist Arshile Gorky—display a distinct improvisational quality. This same preference for spontaneity characterizes Davis's selection of color in his later stripe paintings. Despite their calculated appearance, Davis's stripe works were not based on conscious use of theories or formulas. Davis often compared himself to a jazz musician who plays by ear, describing his approach to painting as 'playing by eye.'
In the 1960s, art critics identified Davis as a leader of the Washington Color School, a loosely connected group of Washington painters who created abstract compositions in acrylic colors on unprimed canvas. Their work exemplified what the critic Barbara Rose defined as the 'primacy of color' in abstract painting.
Although Davis's work from the 1960s—mostly hard-edged, equal-width stripe paintings—is generally viewed in the context of the Washington Color School, his goal differed significantly from the other Color School practitioners. Artists like Morris Louis and Kenneth Noland generally preferred what Noland called 'oneshot' compositions, mostly symmetrical images that could be comprehended at a glance.
In contrast, Davis experimented with complex schemes that lend themselves to sustained periods of viewing. Davis suggested that "instead of simply glancing at the work, select a specific color—and take the time to see how it operates across the painting.—Enter the painting through the door of a single color, and then you can understand what my painting is all about." In discussing his stripe work, Davis spoke not simply about the importance of color, but about 'color interval:' the rhythmic, almost musical, effects caused by the irregular appearance of colors or shades within a composition.
Davis is known primarily for the stripe works that span twenty-seven years, but he was a versatile artist who worked in a variety of formats and media: modular compositions consisting of discrete, but related, pieces that together form one composition; collages combining cutout fragments of images and text with painted and drawn elements; Klee-inspired images that resemble musical scores; and silhouette self-portraits. His works range in scale from miniscule micro-paintings to mammoth outdoor street paintings. Works in other media include printed conceptual pieces, video tapes, and abstract compositions in neon.
In keeping with his unorthodox attitudes, Davis's works do not follow in an orderly sequence. Davis described his method as "a tendency to raid my past without guilt [by] going back and picking up on some idea that I flirted with briefly, say fifteen or twenty years ago. I will then take this idea and explore it more in depth, almost as if no time had elapsed between the present and the time of its original conception." As a result, similar works may be separated by years or even decades. … Davis's works, which resonate with his romantic, free-wheeling approach to art-making, reveal a seriousness balanced by whimsy and an unpredictability that is always a source of joy.
Jacquelyn D. Serwer Gene Davis: A Memorial Exhibition (Washington, D.C.: National Museum of American Art, Smithsonian Institution, 1987)
- Luce Artist Biography
Gene Davis was a journalist before beginning to paint, and worked for a short time as a White House correspondent. He created his first painting when he was twenty-nine, and spent several years experimenting with abstract expressionism. But he later turned away from the lively, expressive style of this movement because he felt it was becoming a cliché. Davis developed his hard-edge stripe paintings in the late 1950s to minimize the effects of brushwork and composition, allowing him to experiment purely with color. He later said that he couldn’t see why “anyone would want to put colors together in any other way.” He created micropaintings, some of which are only a quarter of an inch square, as well as huge installations, including an enormous painting on the road in front of the Philadelphia Museum of Art that required more than four hundred gallons of paint. (Naifeh, Gene Davis, 1982)